Important! Call 911 if you are experiencing any symptoms of a heart attack.
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and the Importance of Screening
What is Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)?
Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) is a simple, non-invasive test that compares the blood pressure in your ankles to the blood pressure in your arms. This test is used to diagnose peripheral arterial disease (PAD), a condition in which the arteries in your legs or arms are narrowed or blocked. PAD can increase your risk of heart attack, stroke, and other serious health problems.
How is ABI measured?
The ABI test is performed by measuring the blood pressure in your arms and ankles using a blood pressure cuff and a Doppler ultrasound device. The ABI is calculated by dividing the systolic blood pressure in your ankle by the systolic blood pressure in your arm. An ABI of 1.0 to 1.4 is considered
normal, while an ABI of less than 0.9 may indicate PAD.
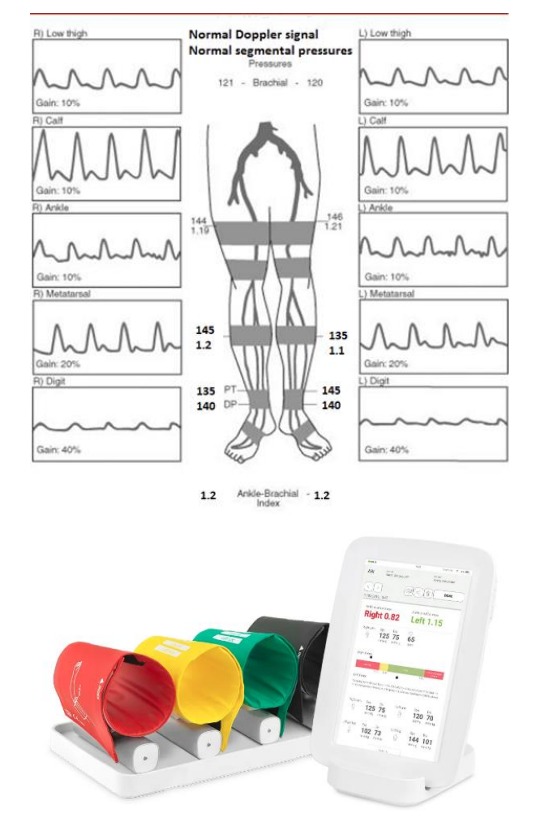
How to interpret ABI results?
1. An ABI of 1.0 to 1.4 is considered normal, while an ABI of less than 0.9 may indicate PAD. If your ABI is less than 0.9, your doctor may recommend further testing to confirm the diagnosis of PAD and determine the best course of treatment.
2. ABI Interpretation:
a. Normal ABI: 0.9 to 1.3
b. Mild PAD: 0.7 to 0.9
c. Moderate PAD: 0.4 to 0.7
d. Severe PAD: Below 0.4
What is Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)?
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries, which can reduce blood flow to the legs and feet. PVD can cause pain, cramping, and fatigue in the legs, and can increase the risk of heart attack
and stroke.
What devices are available for measuring ABI?
There are several devices available for measuring ABI, including the MESI ABI system and the PADnet Express. These devices are designed to provide fast, accurate, and reliable measurements of ABI, helping doctors to diagnose PAD and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
How is PAD treated at Bay Area Heart?
At Bay Area Heart, we are proactive in screening for and treating PAD. Our team of experienced cardiologists uses the latest technology and techniques to diagnose and manage this condition, helping our patients to reduce their risk of serious health problems and improve their quality of life


